Review of Ford 6 Speed Torq Shift Woverdrive
Technically Speaking

- Author: Dale England, ATSG Principal Executive Officer
Preliminary Information
The new Ford 5R110W, referred to past Ford Motor Co. every bit the "TorqShift" transmission, is a redesign of the 4R100 with some previous strategy applied. This unit was introduced in model yr 2003 in the F-Series trucks and Excursions equipped with the new 6.0L diesel engine.
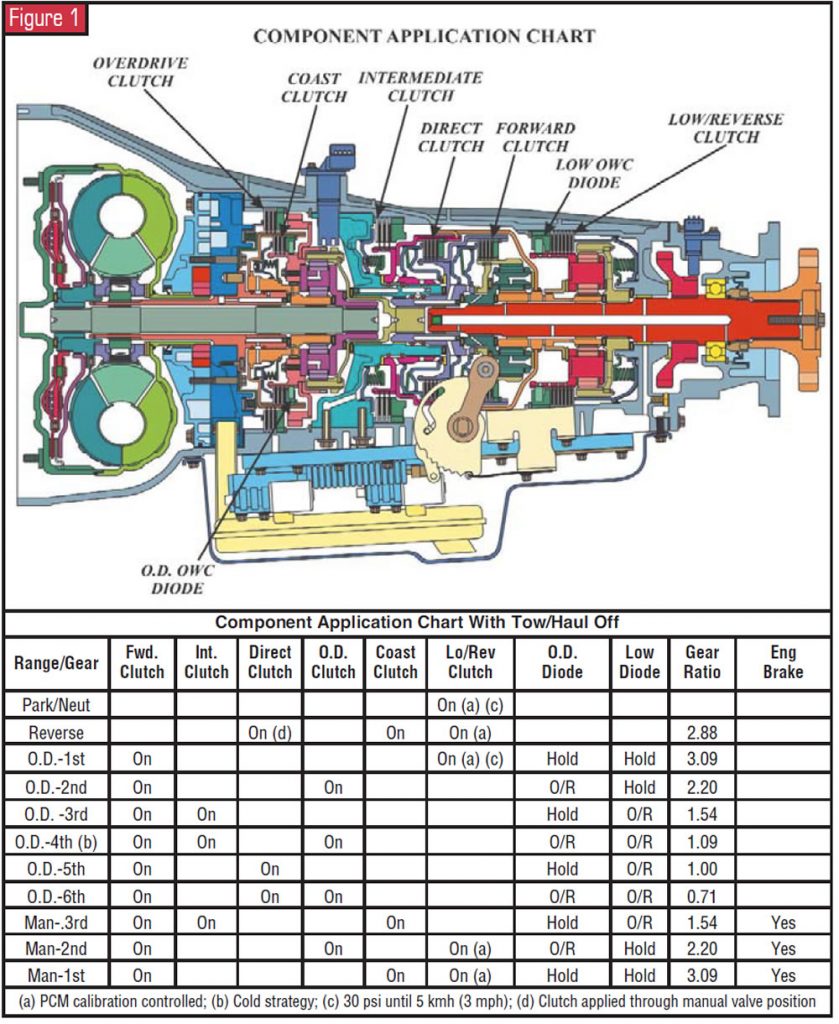
The TorqShift is a v-speed, rear-bicycle-bulldoze unit that really has half dozen forward speeds with ratios depending on whether the transmission is operating in hot or cold manner.. The ratio for 1st gear was changed from two.71 to iii.09. For 2nd gear the overdrive clutch is applied to provide a ratio of ii.twenty. 3rd gear provides a ratio of i.54, the same equally the 4R100'south second gear. All audio familiar? In cold way (below -xv°C (five°F), determined past the transmission-fluid-temperature sensor), the overdrive clutch is engaged in 3rd gear to provide a ratio of i.09 for fourth gear, and the transmission will shift directly from 4th to 6th gear (overdrive), which has a ratio of 0.71. In hot mode the manual volition shift 1st, second, 3rd, fifth (ratio 1.00), 6th.
ATSG's perception of the 2003 Super Duty vehicle that we test drove was that shift performance is profoundly improved over the 4R100 transmission. In that location were no lags betwixt shifts, and every shift was very positive. This is due to a total redesign of the control valve body. A solenoid and a pressure switch are dedicated to the function of each clutch pack, except the frontwards clutch, which is controlled past the manual valve. There are no other shuttle valves in the solenoid body.
Five solenoids control all shifts. Line pressure level and the torque-converter clutch each have their own dedicated solenoid. 4 of the solenoids – TCC, OD clutch, intermediate clutch and the low/reverse clutch – are directly proportional, meaning the pressure output is straight proportional to the applied DC current. The electric current is varied between 0 and one amp from the PCM, and one amp equals maximum pressure in the oil circuit. Three of the solenoids – line force per unit area, coast clutch and direct clutch – are inversely proportional, significant the force per unit area output is inversely proportional to the applied DC electric current. The current is varied between 0 and one amp from the PCM, and 0 amp equals maximum pressure in the oil excursion.
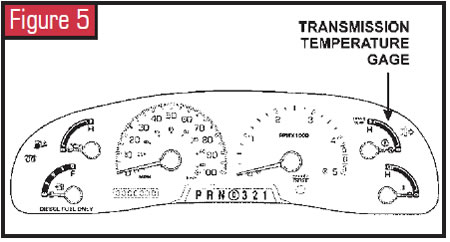
Added to the instrument cluster is a transmission temperature judge that we think is long overdue. Another new feature on this unit is called the tow/booty mode, which is designed to assist the driver when towing a trailer or a heavy load. All transmission gear ranges, including all five forward gears, are available when using the tow/haul feature.
The new manual also uses a new fluid called Mercon® SP, which is not interchangeable with Mercon® or Mercon® V. The utilize of any fluid other than Mercon SP can upshot in abnormal operation and/or transmission failure. Ford recommends replacing the fluid and bottom-pan filter every 48,000 km (30,000 miles) regardless of normal or special operating conditions.
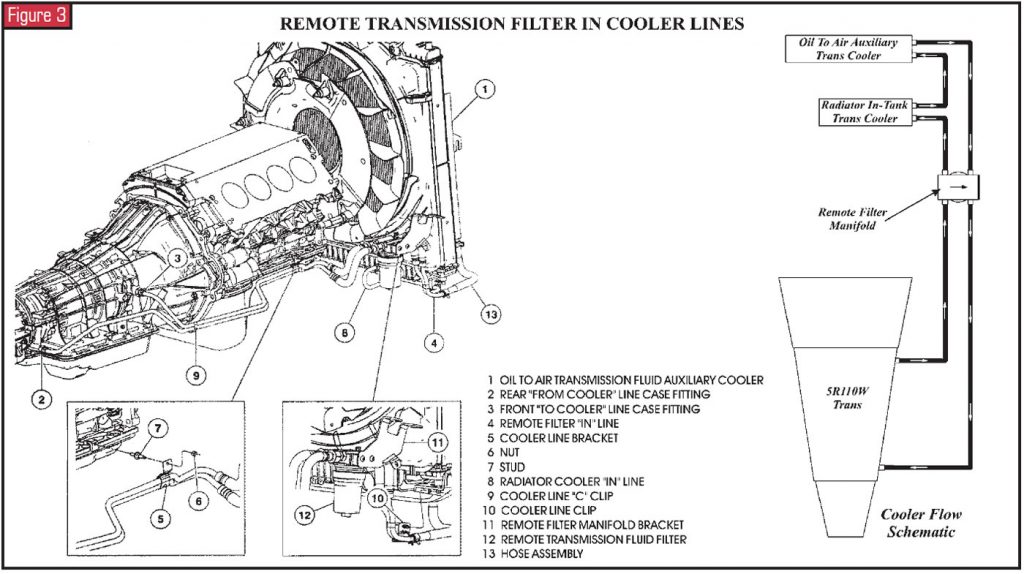
This transmission also is equipped with a new remote fluid filter. This filter passes 10% of the fluid through a small orifice into a serviceable spiral-on filter element. The filtered fluid and so is directed back into the rear lube circuit through the large opening in the remote-filter manifold. The remote filter in the cooler lines also should be replaced at each service interval. This unit is equipped with an oil-to-air (OTA) cooler in forepart of the radiator. Ford recommends replacing the OTA cooler as function of any overhaul or exchange. Do not effort to back-affluent and clean the OTA libation.
General Description and Operation
The TorqShift transmission has seven range positions that can be selected with the manual shift lever: P, R, North, (D), three, 2, ane. A description of each range follows.
- P – In Park, there is no power flow through the transmission. The parking pawl is engaged, locking the output shaft to the manual example. The engine can be started and the ignition key can exist removed.
- R – In Reverse, the vehicle can be operated in a rearward direction at a reduced gear ratio.
- Due north – In Neutral, there is no power menstruum through the transmission. The output shaft is gratis to turn, and the engine can exist started. This position can also exist selected while vehicle is moving, to restart the engine if that becomes necessary.
- (D) – The Overdrive position is the normal position for most forward-gear operations. Information technology provides automatic upshifts and downshifts, utilize and release of the converter clutch, and maximum fuel economy during normal operation.
- 3 – This position provides 3rd-gear start and hold, for improved traction on slippery roads. It also can exist selected at any vehicle speed for improved engine braking. The transmission will non downshift if it would cause an engine-overspeed condition.
- 2 – This position provides second-gear start and hold, for improved traction on slippery roads. Information technology also tin exist selected at whatever vehicle speed for improved engine braking. If this position is selected at higher speeds, the transmission volition downshift to the next-lower gear and will downshift into second gear after the vehicle decelerates to a speed that will not create an engine-overspeed condition.
- 1 – Manual low gear provides 1st-gear operation only. This position also tin be selected at any vehicle speed to provide improved engine braking for descending steep grades. If this position is selected at higher speeds, the manual will downshift to the next-lower gear and will downshift into first gear after the vehicle decelerates to a speed that will not create an engine-overspeed condition.
Bombardment Disconnect, Dead Battery
Any fourth dimension the bombardment is disconnected for any reason, a new PCM has been installed or the calibration has been re-flashed, the adaptive strategy for the "Engagement Schedule" must be updated.
The following procedure will prevent the customer from returning with complaints of business firm or harsh date.
Annotation: All the following engagements must be performed for engagement pressures to adapt correctly with the new calibration.
- Install diagnostic equipment and monitor TFT.
- Warm the manual fluid to 54°C (130°F) as
indicated past the TFT. - Perform 5 engagements from Park to Reverse, each 5 seconds apart.
- Perform 5 engagements from Drive to Reverse, each 5 seconds apart.
- Perform five engagements from Reverse to Drive, each five seconds apart.
- Perform five engagements from Neutral to Drive, each five seconds apart.
Clarification and Performance of Electrical Components
Hither is a brief clarification of each of the sensors and actuators used by the PCM for proper transmission operation:
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
The Powertrain Command Module (PCM) controls the operation of the transmission. Many input sensors provide information to the PCM, which then uses this information to control actuators that determine transmission operation.
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
This sensor is a thermistor in which resistance changes when the temperature changes. The resistance of the sensor increases every bit engine temperature decreases, and the voltage sent to the PCM increases. The PCM uses this information to help determine TCC operation.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
This sensor also is a thermistor in which the resistance changes with temperature. The resistance decreases equally the intake air temperature increases. The IAT provides air-temperature information to the PCM, which uses information technology to help decide transmission line force per unit area and shift scheduling.
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
This sensor is mounted on the accelerator pedal on 6.0-liter diesel applications. The APP sensor detects the position of the accelerator pedal and sends this information as a voltage to the PCM. The PCM uses APP-sensor information to help decide line pressure level, shift scheduling and TCC operation.
Failure of the APP sensor will cause the transmission to operate at a higher-than-normal line pressure to assist avert damage. This will outcome in harsh upshifts and harsh engagements.
Brake Pedal Position Switch
This switch supplies battery voltage to the PCM to bespeak that the brake pedal is applied. The PCM uses this data to release the torque-converter clutch, speed control and auxiliary idle (if the vehicle is and then equipped).
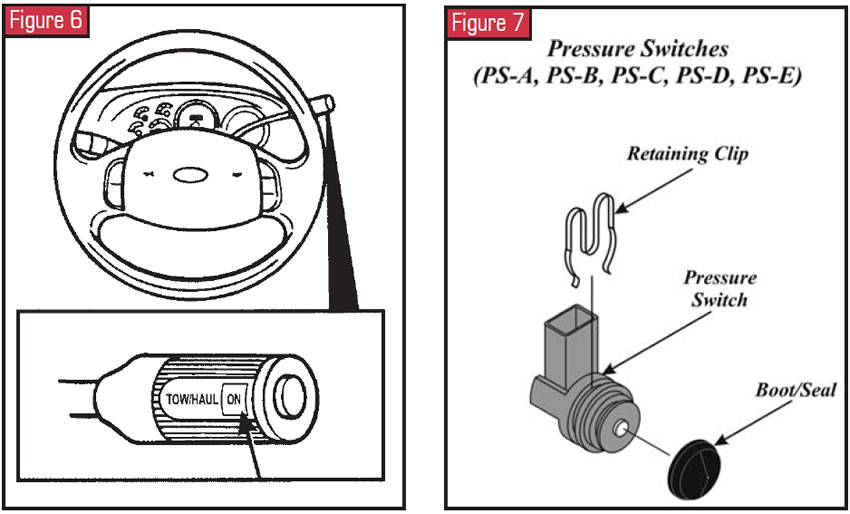
Tow/Haul Switch
This switch on the finish of the manual shift lever is a momentary-contact switch. It provides a signal to the PCM when pressed by the operator, resulting in a change in shift and TCC scheduling. When the tow/haul switch has been pressed, the indicator lamp at the finish of the manual shift lever volition illuminate "Tow/Haul – ON." Pressing the switch once more cancels tow/booty and turns off the TCIL.
Transmission Command Indicator Lamp
With the tow/haul switch on, the indicator lamp at the end of the manual shift lever will illuminate "Tow/Booty – ON." When tow/haul is activated, upshifts occur at a higher vehicle speed, and during deceleration, downshifts besides occur at a higher vehicle speed, providing added engine braking. Pressing the switch again cancels tow/haul and turns off the transmission command indicator lamp (TCIL). The PCM controls the operation of the TCIL. The PCM also may flash the TCIL on and off to alert the driver that a manual operational fault has occurred when it detects certain faults in monitored sensors, solenoids or other transmission components.
4X4 Low Switch
The 4X4 Low Switch, on the instrument panel to the driver'due south right, sends a ground point to the musical instrument cluster when the vehicle is in 4X4 Low. The PCM then receives 4X4 Low status from the musical instrument cluster and adjusts the transmission shift schedule accordingly. Four-wheel "High" can be selected at any vehicle speed upward to 55 mph.
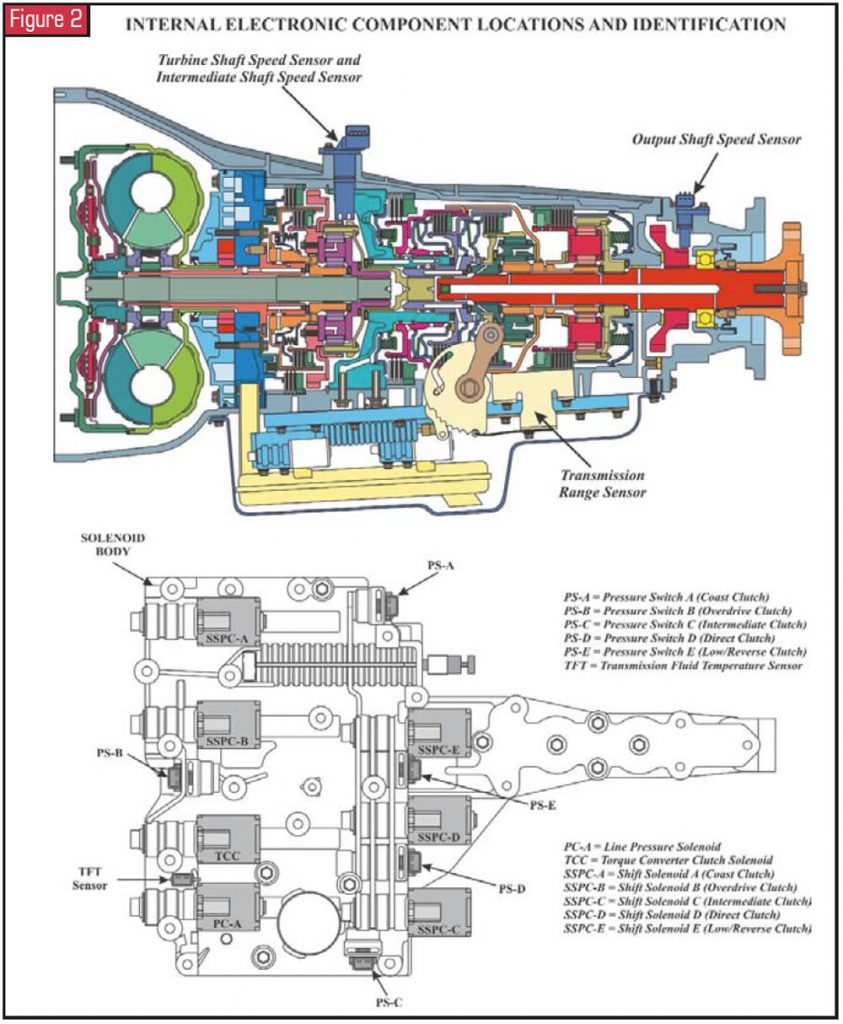
Transmission Solenoid-Body Associates
The solenoid body associates is bolted to the transmission instance within the bottom pan and looks similar to what we accept previously referred to as a valve body. It contains the post-obit:
- Seven variable-force solenoids
- V normally closed pressure switches
- Manual-fluid temperature sensor
- Transmission shift valve
- Overpressurization relief ball.
There is a solenoid and a pressure switch dedicated to the part of each clutch pack, except the frontward clutch, equally it is controlled past the transmission valve. There are no other valves in the solenoid body except for the pressure-relief ball and bound.
The different-design solenoids are keyed differently to prevent misassembly in the solenoid body, and all are retained with a large "E" clip. The "natural"-colored wire connectors connect to the solenoids. The black connectors connect to the pressure switches. There are separate connectors for the TFT sensor and for the TR-P sensor. All of the solenoids except the line-force per unit area solenoid can be serviced without removing the solenoid body from the case.
Line-Pressure level-Command Solenoid
The line-pressure-control solenoid (PC-A) is an inversely proportional three-port solenoid. The pressure output is inversely proportional to the practical DC current supplied through an electronically controlled driver. The current is varied between 0 amp and 1 amp from the PCM, and 0 amp equals maximum force per unit area in the oil excursion. The PC-A solenoid controls the line-pressure oil circuits.
Torque-Converter-Clutch Solenoid
The torque-converter-clutch (TCC) solenoid is a directly proportional iii-port solenoid. The force per unit area output is directly proportional to the applied DC current supplied through an electronically controlled driver. The current is varied between 0 amp and 1 amp from the PCM, and i amp equals maximum pressure in the oil circuit. The TCC solenoid controls the apply and release rates of the converter clutch.
Shift-Solenoid Pressure-Control Solenoids
The overdrive (SSPC-B), intermediate (SSPC-C) and depression/reverse (SSPC-E) clutches are each controlled past a direct proportional 3-port solenoid. The pressure output is directly proportional to the applied DC current supplied through an electronically controlled driver. The current is varied between 0 amp and ane amp from the PCM, and 1 amp equals maximum pressure in the particular clutch oil circuit. The shift solenoid controls the use and release rates of the item clutch pack.
The coast (SSPC-A) and direct (SSPC-D) clutch packs are each controlled by an inversely proportional 3-port solenoid. The pressure output is inversely proportional to the applied DC electric current supplied through an electronically controlled commuter. The electric current is varied between 0 amp and i amp from the PCM, and 0 amp equals maximum pressure in the particular clutch oil circuit. The shift solenoid controls the apply and release rates of the particular clutch pack.
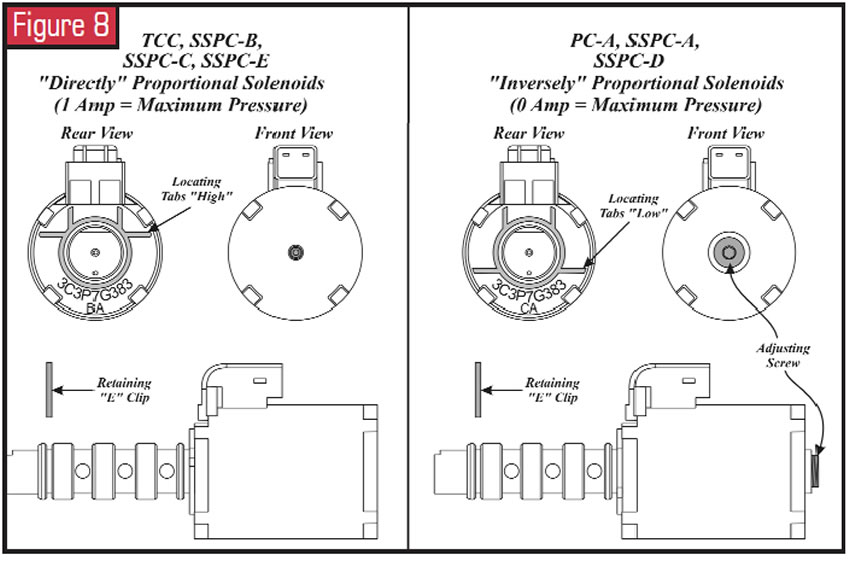
Pressure level Switches
Each of the five shift-force per unit area control solenoids has a corresponding pressure level switch, which is unremarkably closed. The pressure switch is designed to open when shift-solenoid control pressure exceeds 40 psi. All five of the pressure level switches are identical and volition interchange in the solenoid body. Their particular functions follow:
- PS-A = Declension clutch
- PS-B = Overdrive clutch
- PS-C = Intermediate clutch
- PS-D = Directly clutch
- PS-E = Low/Reverse clutch
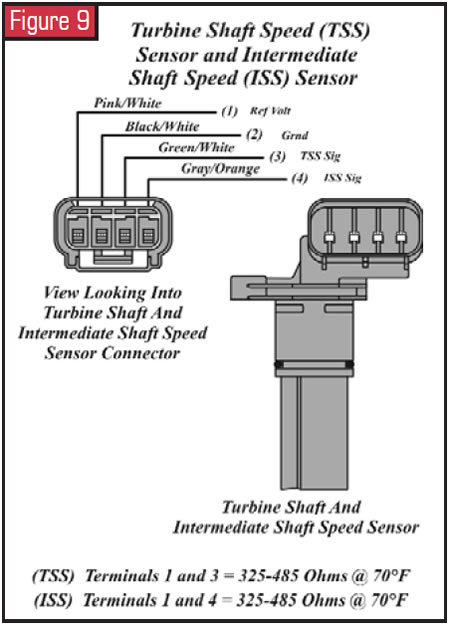
Turbine-Shaft-Speed and Intermediate-Shaft-Speed Sensors
The turbine-shaft-speed (TSS) and intermediate-shaft-speed (ISS) sensors are Hall-effect sensors requiring a 12-volt power supply and a footing. In this unit both sensors are incorporated into one housing. The other two terminals at the sensor are for TSS and ISS signals to the PCM. The sensor detects teeth on the coast-clutch input hub for TSS signal, and the adjacent overdrive ring-gear teeth for the ISS point. Both sensors read 30 teeth per revolution. The TSS/ISS sensors are mounted externally on the transmission example. The TSS/ISS sensors' input to the PCM is digital and used to decide line pressure, shift timing and TCC operation.
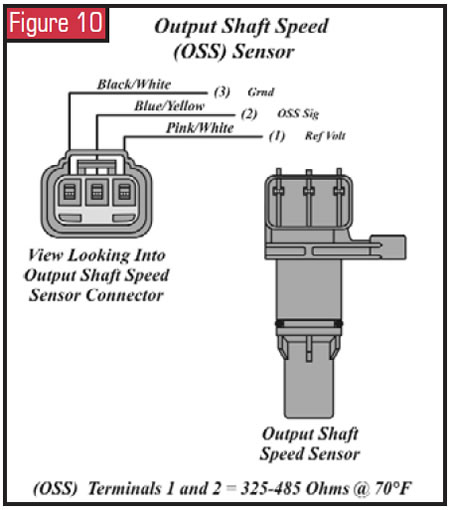
Output-Shaft-Speed Sensor
The transmission output-shaft-speed (OSS) sensor is on the extension housing. The OSS is a Hall-effect sensor. The OSS reads a prepare of gear teeth on the park gear that are different from the teeth used for the park part. The OSS bespeak to the PCM is used for vehicle-speed point, shift scheduling and TCC operation. The OSS has bi-directional capability and uses a digital output.
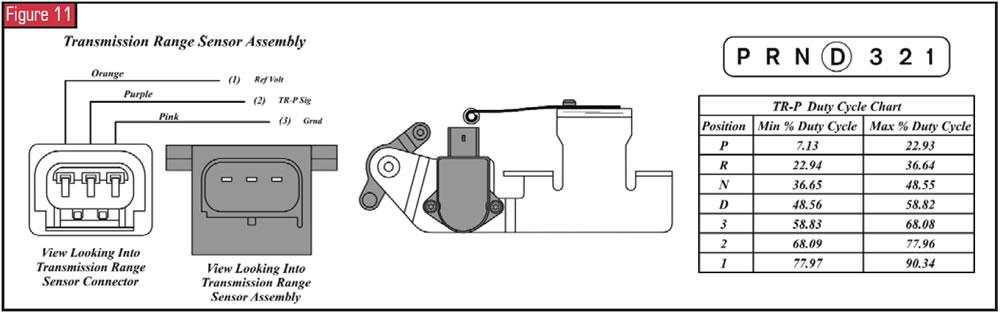
Manual Range Sensor Associates
The transmission-range (TR-P) sensor associates is an internally mounted sensor that includes the detent leap, rooster-comb lever and bracket, side by side to the solenoid body and bolted to the manual case. The transmission-range sensor is non-adjustable and is non serviced independently. The TR-P sensor contains electronic circuitry that provides the PCM a fixed frequency, at a duty cycle, for each of the seven positions of the transmission shift lever. The PCM uses the TR-P sensor signal for starting in Park and Neutral only, reverse-lamp operation, and for line-pressure command, shift scheduling and TCC operation.
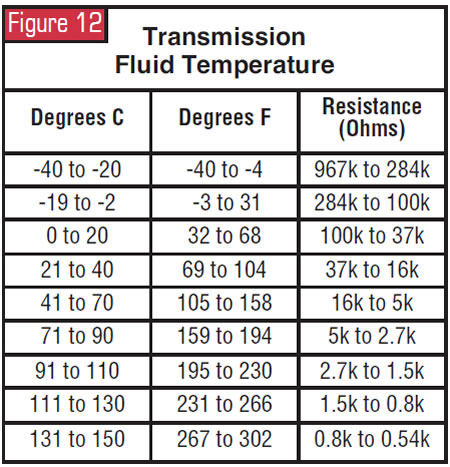
Transmission-Fluid-Temperature Sensor
The TFT sensor twist-locks into the solenoid body and is a temperature-sensitive device called a thermistor. As the fluid temperature increases, the TFT resistance decreases. The PCM uses the TFT signal as an input to decide cold- and hot-temperature shift scheduling and for TCC utilise and release scheduling.

Source: https://www.transmissiondigest.com/ford-5r110w-torqshift/
Enregistrer un commentaire for "Review of Ford 6 Speed Torq Shift Woverdrive"